General Data Protection Regulation (“GDPR” – General Data Protection Regulation – (EU) 2016/679”), which came into force on May 25, 2018, replacing the Directive on the protection of individuals with regard to the processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data No. 95/46/EC. is a binding legal framework applicable to ensure personal data protection residents of European Union (“EU”) member states and European Economic Area (“EEA”).

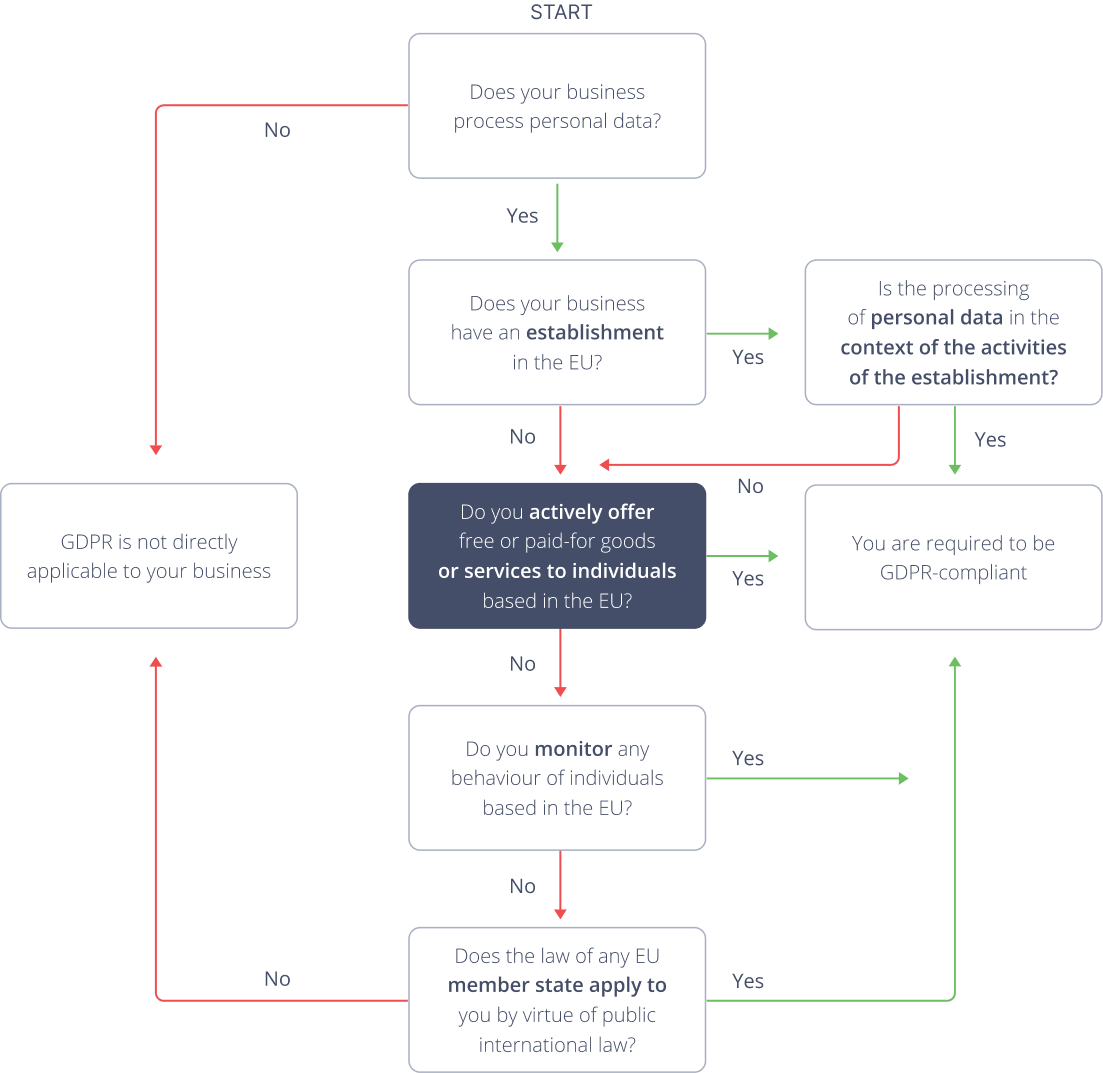
Does your company need to be compliant with the GDPR?
Check by answering these simple questions

GDPR is not directly applicable to your business

No
No
Does your business process personal data?
Yes
Yes
Does your business have an establishment in the EU?
No
No
Do you actively offer free or paid-for goods or services to individuals based in the EU?
Yes
Yes
No
No
Do you monitor any behaviour of individuals based in the EU?
Yes
Does the law of any EU member state apply to you by virtue of public international law?
Is the processing of personal data in the context of the activities of the establishment?

Yes
You are required to be GDPR-compliant

Data controllers / processors, who are subject to important “GDPR” principles such as “Accountability“, “Governance“, and “Transparency“, are as follows:
Appointment of Data Protection Officer / Assigning Data Protection Representative (DPO/DPR)
- In accordance with Article 37 of the GDPR, organizations that carry out regular and systematic processing and large-scale monitoring are required to appoint a DPO and notify the relevant data protection authority.
- Pursuant to Article 27 of the GDPR, organizations established outside the EU but providing goods and services within the EU/EEA must appoint a DPR in the EU.
- The primary role of the DPO is to ensure that the personal data of the organization’s personnel, customers, suppliers or other persons (data subjects) are processed in accordance with the applicable data protection legislation. DPR, on the other hand, acts as a bridge between the relevant EU authorities and data subjects and the organization it represents.
Keeping the Records of Data Processing Activities (Records of Processing Activities)
- It is mandatory to keep a activity record regarding the processed data in organizations with more than 250 employees.
Enforcement of Data Subjects’ Rights
- Individuals are given certain rights over the processing of their data in order to reduce imbalances between data subjects and organizations. These rights such as the right to access their own data, the right to get informed, the right to be forgotten, the right to rectification, the right to data portability, and the right to object. Data controllers have to establish the necessary infrastructures regarding these rights.
Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
- In case of the emergence of new processing activities, data controllers should consider these risks by examining the possible impact of the intended operation before starting the data processing activity. Pursuant to Article 35 of the GDPR, DPIA is required in cases where the relevant data processing activity may pose a high risk to the fundamental rights and freedoms of individuals.
Privacy by Design and Privacy by Default (PbD)
- Organizations are obliged to design processes that will prevent and minimize any risk that may harm the rights and freedoms of data subjects while processing data, and to implement all necessary technical and administrative measures, taking into account the effects of the right to protection of personal data at every stage of data processing.
- The products and services to be provided should be structured according to the risk management-oriented data architecture methodology, which is handled in a way that will comply with the privacy principles from the beginning of the design phase.
- In this respect, it is very important to design business processes in accordance with privacy (Privacy by Design & Privacy by Default) and to establish a solid governance model.
Cross-Border Transfer of Personal Data and Free-Flow of Personal Data
- Mechanisms such as adequacy decision/determining of third countries with adequate protection, standard contractual clauses (SCCs), binding corporate rules (BCR), code of conduct (CoC) and certification mechanisms, and, derogations are the rules set on the GDPR regarding cross-border transfer outside the EEA.
- Organizations that carry out cross-border data transfer should pay the attention to the issue and implement appropriate mechanisms within their establishment.
What Are the GDPR Fines?




How Jurcom Helps You
Our GDPR Consultancy Services include
Compliance Consultancy
Audit and Risk Assessment
Continuous Consultancy
Contact Us Today
Discover how Jurcom can empower your organization with our GRC products and services. Whether you need a reliable compliance solution, robust risk management tools, or expert guidance, we’re here to help you succeed. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward a more secure, compliant, and resilient future for your business.

